Chapter 1 + 2 and Appendix : Introduction, Foundations and Background Material
Independence and Conditional Independence
Independence
- Random variables $X$ and $Y$ are not independent, i.e., $X \not\perp\!\!\!\perp Y$, if there exists two values of $Y$, say $y_1$ and $y_2$, such that $$ P(X \mid Y = y_1) \neq P(X \mid Y = y_2). $$
Number of parameteres of a distribution
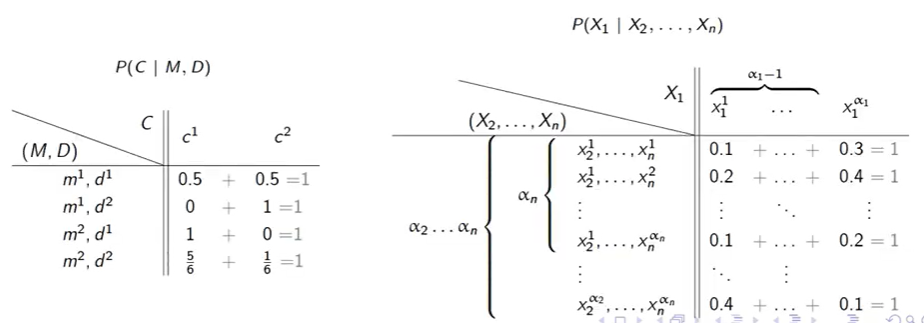
Given discrete random variables $X_1, \dots, X_n$ that take $\alpha_1, \dots, \alpha_n$ values, respectively, number of parameters to represent:
- $P(X_1, X_2, \dots, X_n) \rightarrow \alpha_1 \alpha_2 \dots \alpha_n$.
- $P(X_1 \mid X_2, \dots, X_n) \rightarrow (\alpha_1 - 1) \alpha_2 \dots \alpha_n$.
explain
Information Theory
Deals with efficient coding and transmission of information.
- Encode information to maximize the amount of data that can sent on a given channel.
- Deal with noisy channels.
Compression and Entropy
transmit a large corpus of say English text over a digital line.
Entropy
-
$ P(X) $: distribution over a random variable $ X $.
-
logarithms of base 2. The entropy of $ X $ $$ \boxed{\mathbb{H}_P (X) = \mathbb{E}_P \left[ \log{\frac{1}{P(x)}} \right] = \sum_x P(x) \log{\frac{1}{P(x)}}} $$
-
entropy of $ X $ is the lower bound on the average number of bits required to encode values of $ X $.
-
entropy is as a measure of our uncertainty about the value of $ X $.
Proposition $$ 0 \leq \mathbb{H}_P (X) \leq \log{|Val(X)|} $$
Joint Entropy
- $ X_1, \dots, X_n $: random variables. The joint entropy of $ X_1, \dots, X_n $
$$ \boxed{\mathbb{H}_P (X_1, \dots, X_n) = \mathbb{E}_P \left[ \log{\frac{1}{P(X_1, \dots, X_n)}} \right]} $$
Capture how many bits are needed (on average) to encode joint instances of the variables.
Conditional Entropy
The additional cost (in terms of bits) of encoding $ X $ when we already encoding $ Y $ $$ \begin{align*} P(X, Y) = P(Y) \cdot P(X \mid Y) &\Leftrightarrow \log{\frac{1}{P(X, Y)}} = \log{\frac{1}{P(Y)}} + \log(\frac{1}{P( X \mid Y )}) \\ &\Leftrightarrow \mathbb{H}_P (X, Y) = \mathbb{E} \left[ \log{\frac{1}{P(Y)}} \right] + \mathbb{E} \left[ \log(\frac{1}{P( X \mid Y )}) \right] \\ &\Leftrightarrow \boxed{ \mathbb{H} ( X \mid Y ) = \mathbb{E} \left[ \log{\frac{1}{P( X \mid Y )}} \right] = \mathbb{H} (X, Y) - \mathbb{H} (Y) } \end{align*} $$
Entropy Chain Rule
$$ \boxed{ \mathbb{H} ( X_1, \dots, X_n) = \mathbb{H}(X_1) + \mathbb{H} (X_2 \mid X_1) + \dots + \mathbb{H} (X_n \mid X_1, \dots, X_{n - 1}) } $$
Intuitively, we would expect $ \mathbb{H} (X \mid Y) $ to be at least as small as the cost of encoding $ X $ alone $$ \mathbb{H} (X \mid Y) \leq \mathbb{H} (X) $$
Mutual information
The mutual information between $ X $ and $ Y $ $$ \boxed{ \mathbb{I}(X ; Y) = \mathbb{H}(X) - \mathbb{H}(X \mid Y) = \mathbb{E} \left[ \log{\frac{P(X \mid Y)}{X}} \right] } $$
Captures how many bits we save (on average) in the encoding of $ X $ given $ Y $. The mutual information statisfies:
- $ 0 \leq \mathbb{I}(X; Y) \leq \mathbb{H}(X) $.
- $ \mathbb{I}(X; Y) = \mathbb{I}(Y; X) $.
- $ \mathbb{I}(X; Y) = 0 $ iff $ X $ and $ Y $ are independent.
$ \rightarrow $ view mutual information as a quantitative measure of the strength of the dependency between $ X $ and $ Y $. The bigger the mutual information, the stronger the dependency.
- The extreme upper value of the mutual information is when $ X $ is a deterministic function of $ Y $ (or vice versa) $ \rightarrow \mathbb{I}(X; Y) = \mathbb{H}(X) $
Relative Entropy and Distances Between Distributions
Distance Metric
A distance measure $ d $ that satisfies:
- Positivity: $ d(P, Q) $ is always nonnegative, and is zero iff $ P = Q $.
- Symmetry: $ d(P, Q) = d(Q, P) $.
- Triangle inequality: for any three distributions $ P, Q, R $, $$ d(P, R) \leq d(P, Q) + d(Q, R). $$
Relative Entropy
- $ P $: the true distribution that generates the data.
- $ Q $: approximation or guess for the true distribution (learned from data).
- $ \mathbb{H} (X) $: how many bits required (on average) to encode outcomes optimally assuming known $ P $.
However, we often don’t know $ P \rightarrow $ use $ Q $.
Question: How much we lost, due to the inaccuracy of using $ Q $?
The relative entropy of $ P $ and $ Q $
$$ \boxed{ \mathbb{D}(P(X_1, \dots, X_n) || Q(X_1, \dots, X_n)) = \mathbb{E}_P \left[ \log{\frac{P(X_1, \dots, X_n)}{Q(X_1, \dots, X_n)}} \right] } $$
Short hand notation, $$ \mathbb{D}(P || Q) $$
Properties
- $ D(P || Q) \geq 0 $ (Gibb’s inequality).
- $ D(P || Q) = 0 $ iff $ P = Q $.
- $ D(P || Q) \not= D(Q || P) $: Asymmetric.
Relative entropy is not a distance measure over distributions since it does not satisfy:
- symmetry,
- triangle property.
Continuous Optimization
Characterizing Optima of a Continuous Function
Maximization/minimization problems:
- Find values $ \theta_1, \dots, \theta_n $ st $$ f_{\text{obj}} = \max_{\theta_1, \dots, \theta_n} f_{\text{obj}} (\theta_1, \dots, \theta_n) $$
sum of squared distances example
- $ (x[1], y[1]), (x[2], y[2]), \dots, (x[m], y[m]) $: set of $ m $ points in 2D space.
- Goal: Find the centroid of these point: $ (\theta_x, \theta_y) $ st the sum of squared distances from each point to this centroid is minimized.
Formulate this problem into a maximization problem by considering the negative of the sum of squared distances: $$ f_{\text{obj}} (\theta_x, \theta_y) = - \sum_i \left( (x[i] - \theta_x)^2 + (y[i] - \theta_y)^2 \right) $$
At the maximum, the gradient of function (vector of partial derivatives) $ f_{\text{obj}} (\theta_1, \dots, \theta_n) $ is 0, $$ \nabla f = \left\langle \frac{\partial f}{\partial \theta_1}, \ldots, \frac{\partial f}{\partial \theta_n} \right\rangle $$
Constrained Optimization
Optimizing a continuous function over its entire domain, under a set of equally constraints.
Find $ \theta $
Maximizing $ f(\theta) $
subject to $$ c_1 (\theta) = 0 $$
$$ \cdots $$
$$ c_m (\theta) = 0 $$
Rephrase equality constraint as constraining a function $ c $ to 0 $$ \mathcal{C} = \{ \theta : \forall j = 1, \dots, n, c_j (\theta) = 0 \} $$