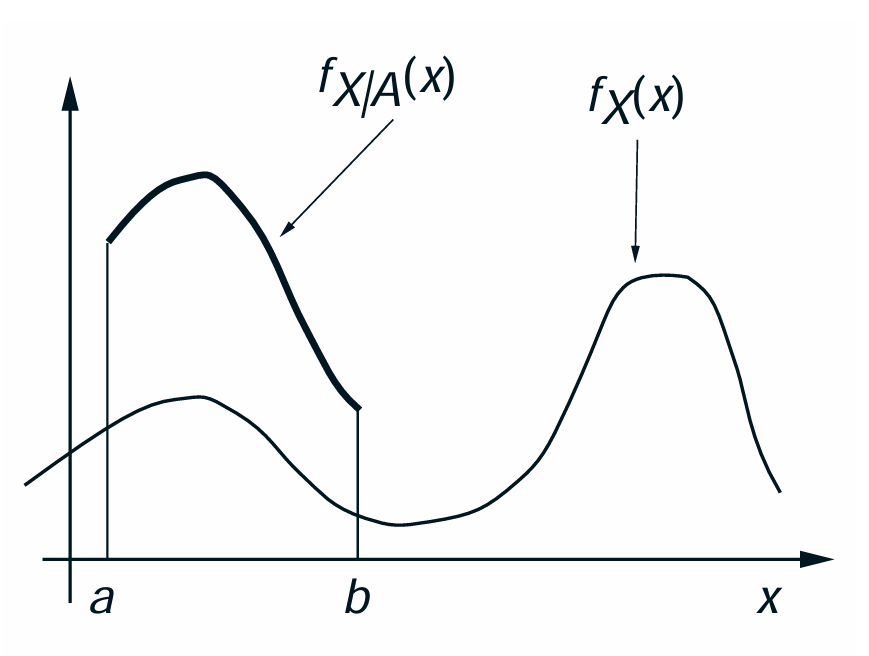
- The conditional PDF is zero outside the conditioning set $ A = [a, b] $.
- Within the conditioning set
- same shape as the unconditional one
- but scaled by constant factor $ 1 / P(X \in A) \rightarrow $ ensures $ \int f_{X \mid A} (x) \, dx = 1 $.
Lecture 9 + 10: Joint Distribution, Conditioning and Independence
Conditioning on an Event
$$ p_X (x) = P(X = x) $$
$$ \boxed{ p_{X \mid A} (x) = P(X = x \mid A) } $$
$$ P(X \in B) = \sum_{x \in B} p_X (x) $$
$$ \boxed{ P(X \in B \mid A) = \sum_{x \in B} p_{X \mid A} (x) } $$
$$ \boxed{ \sum_x p_{X \mid A} (x) = 1 } $$
$$ f_X (x) \cdot \delta \approx P(x \leq X \leq x + \delta) $$
$$ \boxed{ f_{X \mid A} (x) \cdot \delta \approx P(x \leq X \leq x + \delta \mid A) } $$
$$ P(X \in B) = \int_B f_X (x) \, dx $$
$$ \boxed{ P(X \in B \mid A) = \int_{B} f_{X \mid A} (x) \, dx } $$
$$ \boxed{ \int f_{X \mid A} (x) \, dx = 1 } $$